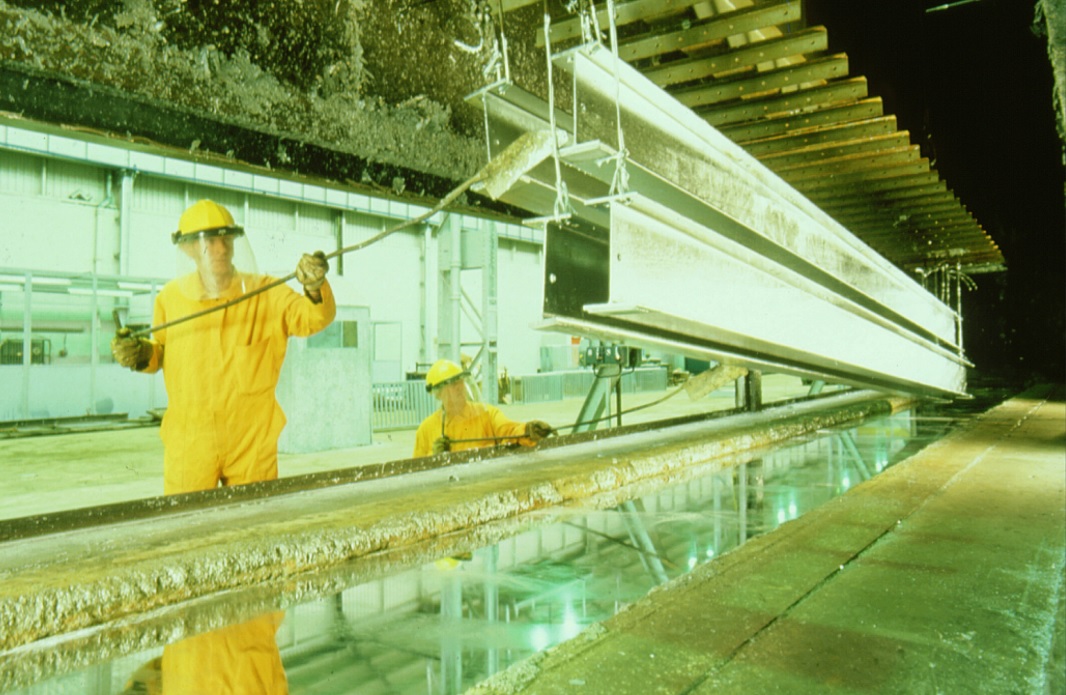
It is common misconception that any zinc coating can be termed as galvanizing but this is in fact not the case as there are many different processes by which a zinc coating may be applied. Hot Dip Galvanizing refers only to coatings formed by immersing steelwork into molten zinc. However, there are two variations of the Hot Dip Galvanizing processes: Batch Galvanizing and Pregalvanizing.
Batch Hot Dip Galvanizing
This process is used to coat fully fabricated articles and involves chemical cleaning of work prior to immersion in the galvanizing bath and is specified by EN ISO 1461. This process described in this article provides complete coverage of the article (including internal surfaces of hollow sections) with no uncoated area being present. The thick coating formed also offers the highest level of corrosion protection available.
Pregalvanized Steel Product
An alternative is to take a specific product (typically sheet, wire or tubes) and galvanize them using an automated process.
Pre galvanized Steel Sheet
This is the most widely used pregalvanized product and is specified by EN 10346. Sheet is uncoiled and passed through a reducing atmosphere prior to immersion in the galvanizing bath for a relatively short period of time. Upon withdrawal from the galvanizing bath, either an air knife or mechanical wiper is used to remove excess zinc so producing a good surface finish. The result however is a thin coating which may vary from 7-42 μm according to grade with most products typically having a coating thickness of 20 μm. After galvanizing, the sheet is recoiled prior to a stockholder, the sheet being uncoiled and cut for sale so producing uncoated edges.
Pregalvanized Steel Tubes
Tubes may also be galvanized using an automated process to EN 10240. Again Immersion times are relatively short and upon withdrawal, steam may blown down the bore of the tube to give an adequate surface finish. The coating thickness may be as high as 45-55 μm although much of the product produced has a significantly thinner coating of 20-30 μm. Again for resale purposes, tubes may be cut to size creating uncoated edges.
Pregalvanized wire
From a practical point of view strands of wire may only be coated using an automated process and this may be specified by EN 10244-2. Immersion times are again short with wiping procedures being utilized to remove excess zinc and achieve a smooth finish. Coating thickness may vary with grade and strand diameter but might typically be circa 20-30 μm. Note that while individual strands can not be galvanized to EN ISO 1461 mesh might be suitable for such processing so achieving a thicker galvanized coating.
Coating Comparison
Both batch hot dip galvanizing and pregalvanized coatings have different characteristics and the table below summarises these.
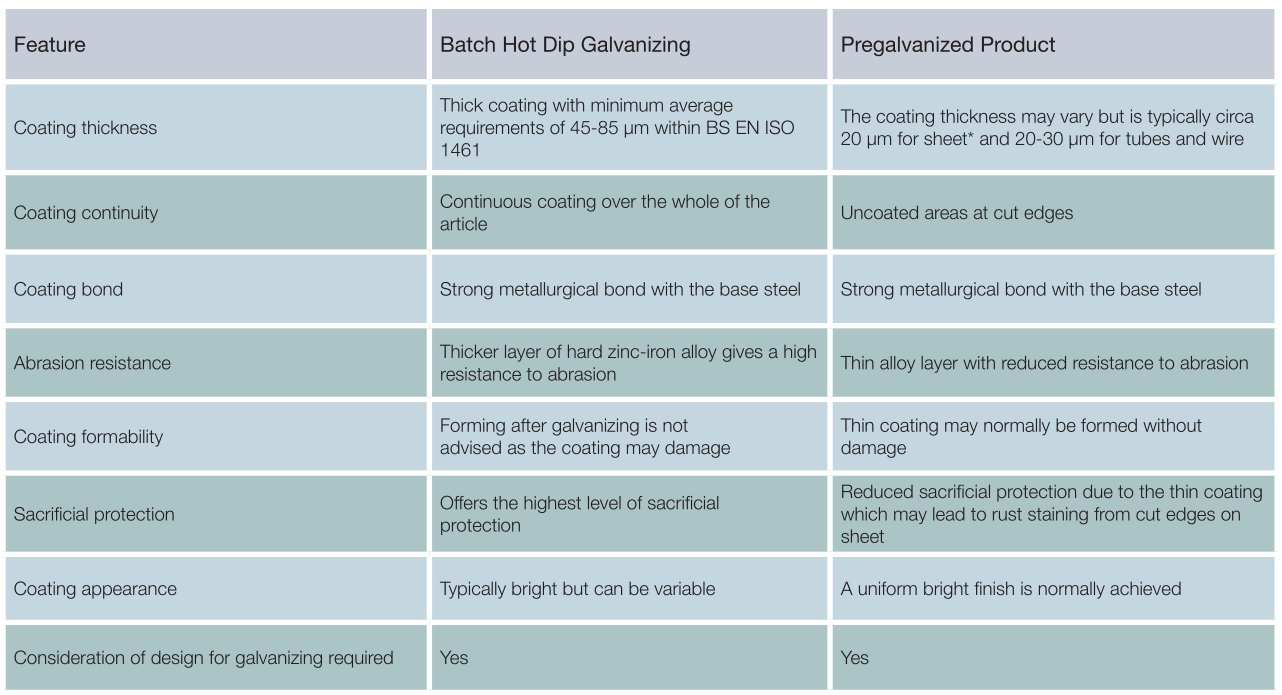
*It is important to remember that when coating weights are specified for steel sheet, the weights include both sides of the sheet so that the life of the coating is half that for the equivalent coating weight specified in EN 10346
Learn more
You can find more information about Hot Dip Galvanizing on Galvanizing Association website. Advice is alsoavailable from GA to ensure optimum design of components.